- English
- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
asi tipu uku
Te Maramatanga ki nga Tipu Uku ASI: Nga Maramatanga mai i te Marae
He mea nui nga tipu ASI i roto i nga hanganga hou, engari he maha nga taangata kei waho o te umanga ka warewarehia ki o raatau uaua. Ka rukuhia e tenei tuhinga nga ahuatanga o ASI tipu uku, te whakamahi i nga wheako mahi me nga akoranga i akohia i roto i te waa. Mai i nga mahi mahi ki nga wero ohorere, he maha nga mea hei wetewete.
Ko te Core o nga Tipu Uku ASI
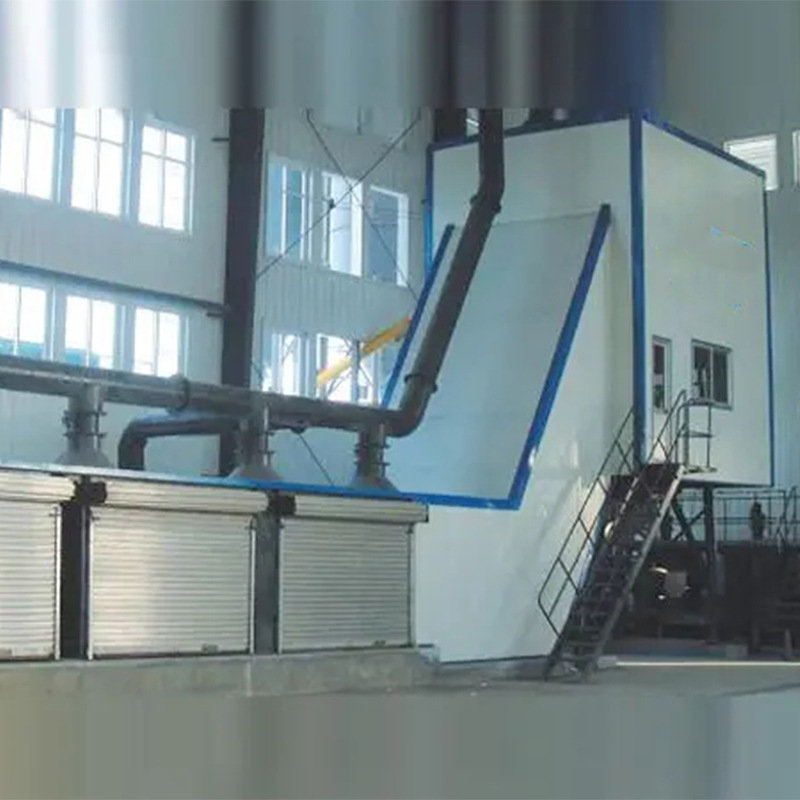
-1Ka tiimata me nga mea taketake, ASI tipu uku he mea nui ki te whakaputa i te ranunga uku e hiahiatia ana mo te hanga rori. Ko ia tipu, i runga i te tauira me te hanga, kei a ia ano nga ahuatanga motuhake. Hei tauira, ko te tatūnga i Zibo Jixiang Machinery Co., Ltd., he kaihautū ki te hanga mihini whakaranu raima i Haina (he maha nga korero kei to ratou paetukutuku), he whakatauira i te huarahi whakauru pai ki te whakaranu me te kawe.
Ko tetahi pohehe noa e mahi ana nga tipu uku hei wae motuhake. I roto i te meka, ka hiahia ratou ki te hononga tohu me nga punaha waka, nga kaiwhakarato rauemi mata, me nga raarangi hanga. Ko te kore e aro ki tenei hononga-a-iwi ka arahi ki nga ngoikoretanga me nga whakaroa, ka nui te utu i roto i nga kaupapa nui.
He maha nga wa ka kitea e nga maaramatanga mahi te hiahia mo te tiaki me te whakahou i nga wa katoa. Ka takamuri pea nga tauira tawhito ki nga tauira hou me nga punaha whakahaere matatau me nga ahuatanga hanganga ture. Kaore e taea te whakanui ake i tenei waahanga ki te pupuri i te tipu ki te whakataetae me te whai hua.
Nga Wero Whakahaere me nga Whakataunga
Ko te whakahaere i nga rauemi mata tetahi waahanga e raru tonu ana. Ko te kounga whakahiato, nga taumata makuku, me te whakahaere i te pāmahana ka tino pa ki te kounga o te hua whakamutunga. Kei te maumahara ahau ki tetahi kaupapa i puta ai nga rereketanga o nga wa tuku whakahiato ki te koretake o te ranunga. Ko te whakamaarama i enei take he maha nga wa e tika ana te whakarite me te aro turuki, me te hono tata ki nga kaiwhakarato me nga kamupene taraka.
Ko nga mahi hokohoko kaore e taea te karo. Ko te whakataurite i te tere whakangao me te mana o te kounga he uaua, ina koa i raro i nga ra kati. Ma te whakamahi i nga hoahoa taapiri, penei i te kite i etahi tipu Zibo Jixiang Machinery Co., Ltd., ka taea te ngawari. Ko enei waahanga ka whakahaere i nga whakarereketanga tere me te kore e aukati i te mahi tonu.
He keehi motuhake i te korenga o nga taputapu ohorere i hiahia kia huri wawe ki nga mana whakahaere a-ringa. I whakanuia e taua ra te hiranga o te whakangungu me nga kaiwhakangungu whakawhiti ki te hapai i nga ahuatanga ohorere, me te whakarite kia mau tonu.
Nga Whakaaro Taiao
Na te piki haere o nga ture taiao, ASI tipu uku me urutau. Ko nga punaha kohinga puehu, nga hangarau whakaheke haruru, me nga whakahaere tukunga kua waiho hei whakaritenga paerewa. Kare e ranea ki te whakatutuki i nga paerewa o naianei; he mea nui te tatari mo nga huringa ture a meake nei.
I roto i nga mahi, ko te whakahou i nga tipu tawhito me nga hangarau taiao ka taea te wero engari he utu. Ko enei whakamohoatanga ehara i te mea ka whakapai ake i nga hanganga ture engari he maha nga wa ka pai ake te kaha o te kaha me te penapena utu mo te wa roa.
I tua atu, ko nga hononga hapori ka whakawhirinaki ki te tapuwae taiao o te tipu. Ko nga whakamohiotanga a te iwi i ia wa, me nga korero marama mo nga mahi ki te whakaiti i te paanga he tino rautaki mo te whakatipu whanaungatanga pai.
Te Whakanekehanga Hangarau
Kei te huri haere tonu te whakaurunga hangarau ASI tipu uku. Ko nga punaha whakahaere me nga punaha aroturuki-a-waa e pai ana ki te arotau i nga putanga me te whakarite i te kounga o te kounga. Heoi, he pai noa te hangarau ki tana kaiwhakamahi. Ko te whakangungu tika me te tirotiro i nga punaha i ia wa ka aukati i nga rawa hangarau kia noho taunaha.
Ko tetahi tauira whaihua ko te whakamahi i te rorohiko tiaki matapae, he huringa keemu ki te tautuhi i nga take ka taea. Ehara i te mea ka whakaiti noa i te waa, engari ka roa ake te oranga o nga taputapu me te whakapai ake i te haumaru.
Ko nga haumi i roto i enei hangarau me hono ki nga whaainga pakihi. He akoranga i akohia mai i te wheako: ko te hangarau mo te hangarau he uaua te utu ki te kore he tino whainga me te mahere pakari mo te whakauru me te whakamahi.
Ko te Take Tangata i roto i nga Tipu Uku ASI
Ahakoa te ahu whakamua i roto i te mahi aunoa, he mea nui tonu te huānga tangata. Ka taea e nga kaiwhakahaere mohio te whakarereketanga maataki i runga i nga huringa ngawari o nga ahuatanga o nga taonga me nga oro taputapu—nga kaha ka uaua tonu te hangarau ki te whakataurite.
Ko nga kaupapa whakangungu me whakahou tonu ki te whakauru i nga paerewa ahumahi me nga hangarau hou. Karekau he whakakapinga mo te wheako i runga i te mahi, he mea ka taea e nga kaiwhakahaere rangatahi ma te mahi i te taha o nga tohunga mohio.
Ko te tikanga, ASI tipu uku he puunaha rauwiringa kaiao e tika ana kia taurite te hangarau, nga pukenga tangata, me te whakahaere rautaki. Ko te ahua hihiri o tenei mara he mea whakawero, he utu hoki, na ia kaupapa e tuku akoranga hou me nga tirohanga.
E pa ana Hua
Hua e Pa ana
Hoko Pai Hua
Nga Hua Hoko Pai-
![[Copy] Kaiwehe kirikiri](https://www.zbjxmachinery.com/wp-content/uploads/1-115.jpg) [Copy] Kaiwehe kirikiri
[Copy] Kaiwehe kirikiri -
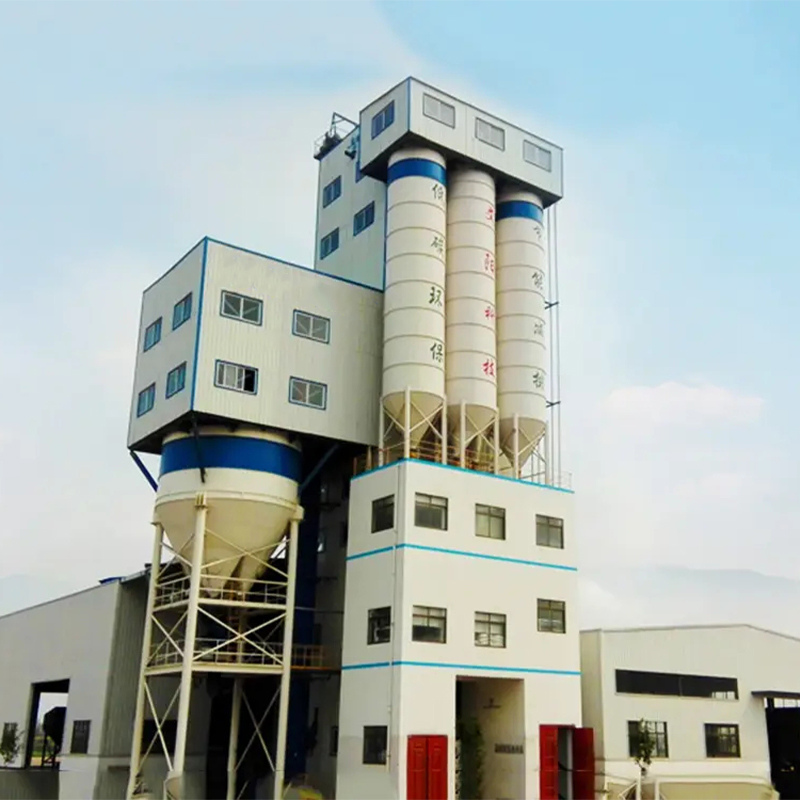
 S RANGA SJHZS120S
S RANGA SJHZS120S -
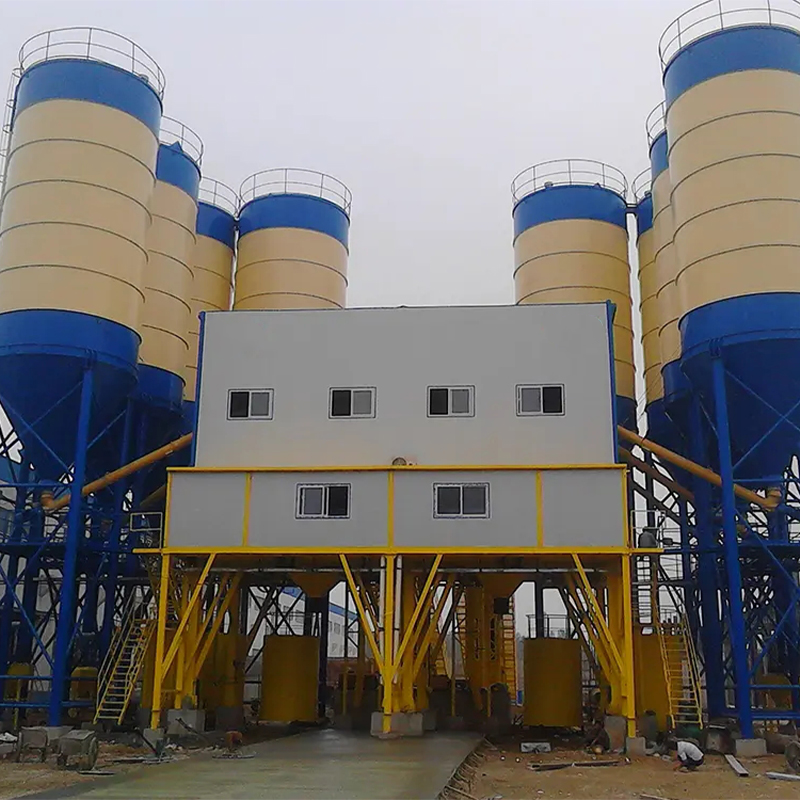
 Waahi Peke Raima
Waahi Peke Raima -
 TARAKI WHAKANUI RIMAHI HIKO C410-D28F 10M³ 8×4
TARAKI WHAKANUI RIMAHI HIKO C410-D28F 10M³ 8×4 -
 SjGJD060-3GStepped Momo moata maroke te Tipu Whakapae
SjGJD060-3GStepped Momo moata maroke te Tipu Whakapae -
 S Rangatū SjHZN120S
S Rangatū SjHZN120S -
 Te Teihana Waea Pukoro Hiki
Te Teihana Waea Pukoro Hiki -
 Whakaranu Taraka Raima 6×4
Whakaranu Taraka Raima 6×4 -
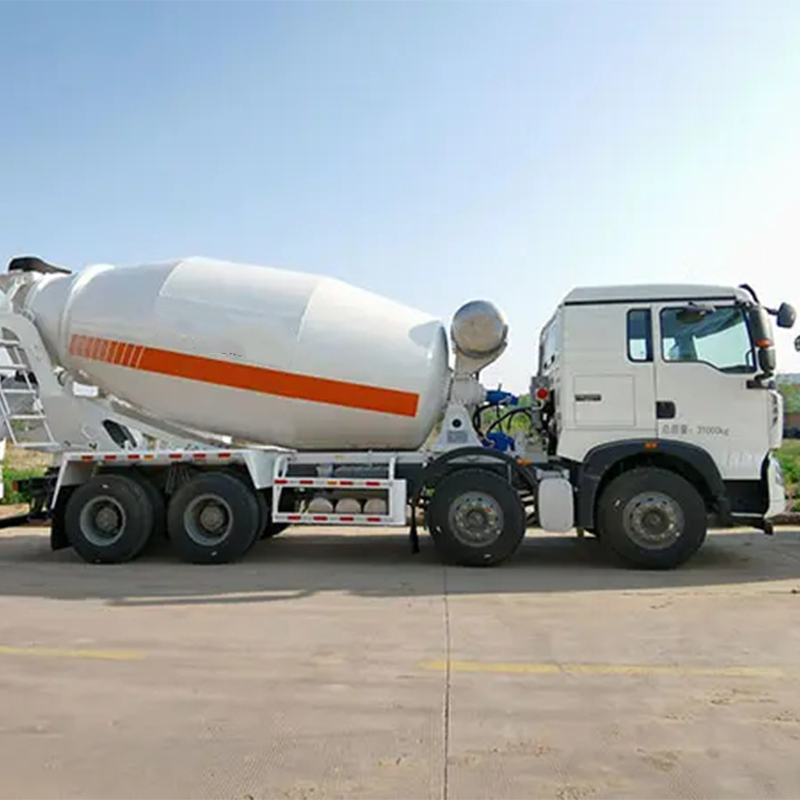 Raima Taraka Raima
Raima Taraka Raima -
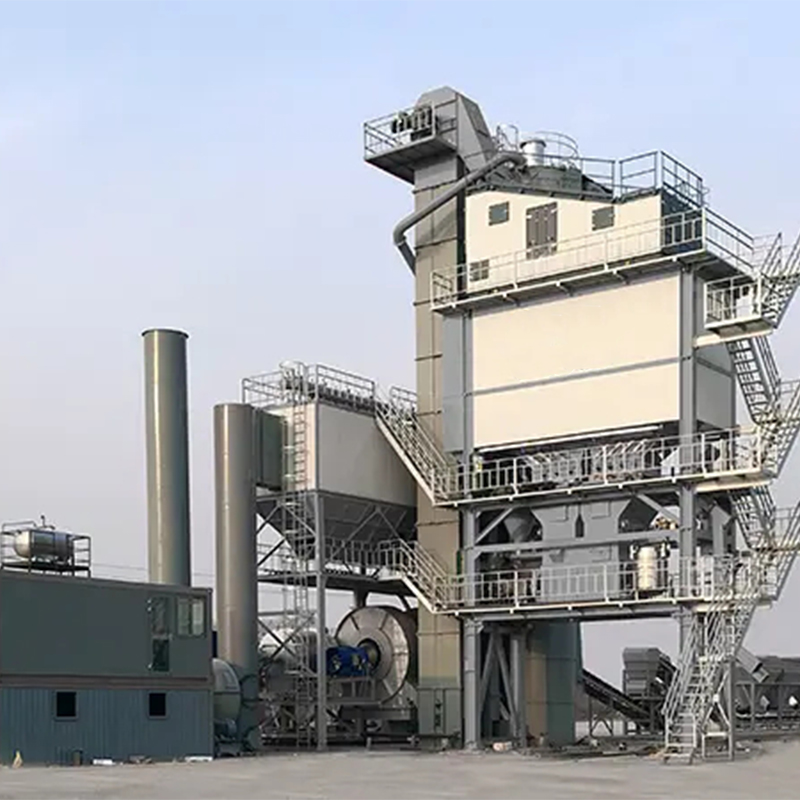 Tipu Tipu Uku SjLBZ240/3205B
Tipu Tipu Uku SjLBZ240/3205B -
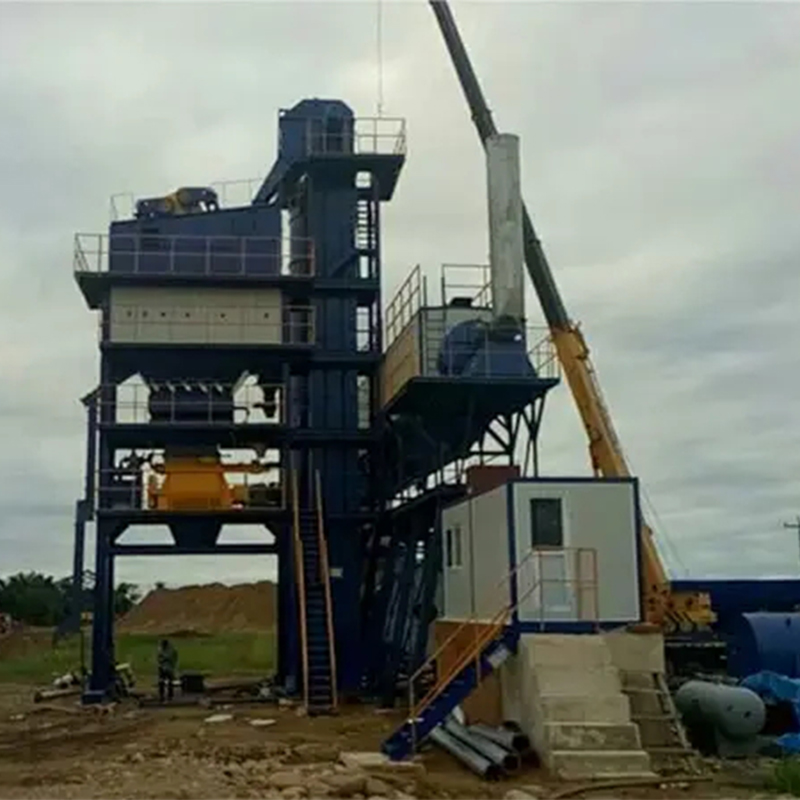 Tipu Tipu Uku SjLBZ160/180-5B
Tipu Tipu Uku SjLBZ160/180-5B -
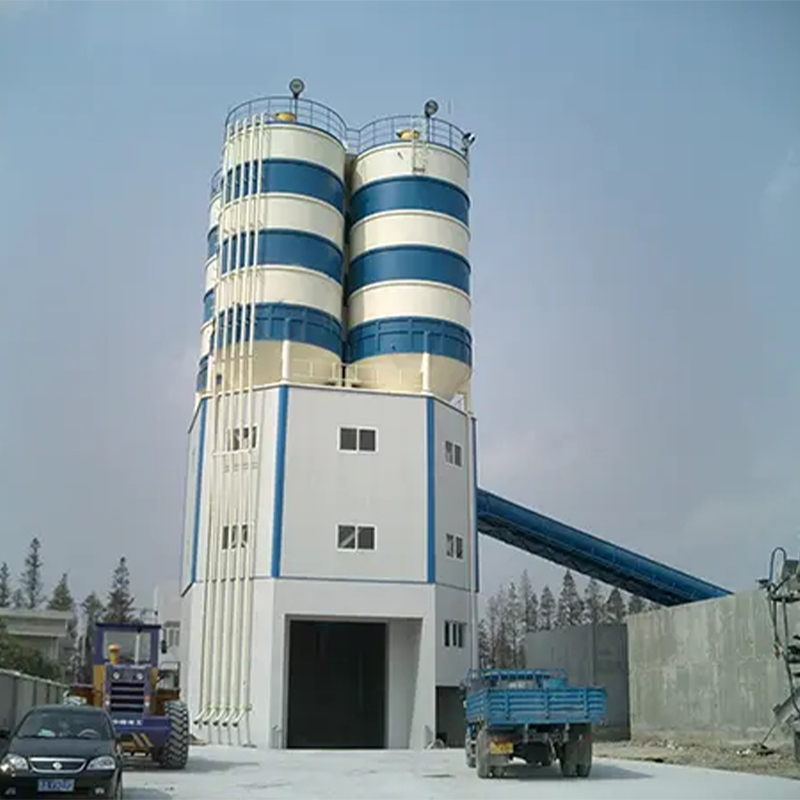 D Series Cement Silo Momo Runga SjHZS120D
D Series Cement Silo Momo Runga SjHZS120D